The difference between MGO and UMF in Manuka Honey
The number of manuka honey products being sold is 10 times higher than the actual global production. This discrepancy raises concerns about the authenticity of manuka honey products, potentially leading to the purchase of counterfeit honey that may not deliver the full spectrum of health benefits associated with genuine manuka honey.
Manuka Honey is authenticated through industry-standard grading systems such as Unique Manuka Factor (UMF) or methylglyoxal (MGO) content, ensuring its quality and certifying its genuine origin. There is often confusion about the difference between the two terms and it can make it difficult to know which honey to buy.
In this blog, we will be diving into the health benefits of Manuka Honey, and what these two grading systems mean to help you discover the best and most authentic honey!
What is Manuka Honey?
Manuka Honey is a type of honey which is native to New Zealand, produced by bees which pollinate the flower Leptospermum scoparium, also known as the Manuka Bush. For Manuka Honey to be labelled as Manuka, it must be exclusively sourced from the nectar of the Manuka flower and be monofloral.
What is the difference between manuka honey and honey?
Manuka honey offers more antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties than regular honey which can be attributed to the following:
Methylglyoxal (MGO):
Methylglyoxal is the ingredient in Manuka Honey which provides its antibacterial and antimicrobial properties. It is formed from the conversion of dihydroxyacetone (DHA). Generally, the higher the MGO level, the higher the antibacterial properties of the honey. Methylglyoxal is also used to measure the plant phenol activity.
Hydrogen Peroxide:
While regular honey relies on hydrogen peroxide for its antibacterial benefits, manuka honey has low levels of hydrogen peroxide as it does not accumulate in it. Additionally, hydrogen peroxide can be easily broken down, posing a risk of the honey losing its antibacterial properties.
Flavonoids and Phenolic Compounds:
Manuka Honey contains a higher concentration of phenols and flavonoids compared to regular honey. This high content of phenols results in the high antioxidant and antibacterial levels.
What are the benefits of Manuka Honey?
With abundant levels of methylglyoxal, flavonoids and phenols, Manuka honey provides a myriad of health advantages. It proves effective in accelerating wound healing, preventing infections, and alleviating pain, thereby contributing to the fight against antibiotic resistance in wound care.
Additionally, its potent antibacterial properties aid in reducing gum inflammation and inhibiting harmful bacteria growth. The anti-inflammatory and antibacterial attributes make Manuka Honey a soothing remedy for sore throats and coughs.
Studies also suggest its potential in promoting a healthy gut by acting as a prebiotic, reducing inflammation, abdominal pain, and diarrhoea associated with infection-causing strains.
How is Manuka Honey graded?
Manuka Honey is graded either by MGO or UMF. These grading systems are a way to distinguish the antibacterial properties and potency of each batch of honey. It also allows consumers to identify if the honey is authentic.
MGO Grading of Manuka Honey:
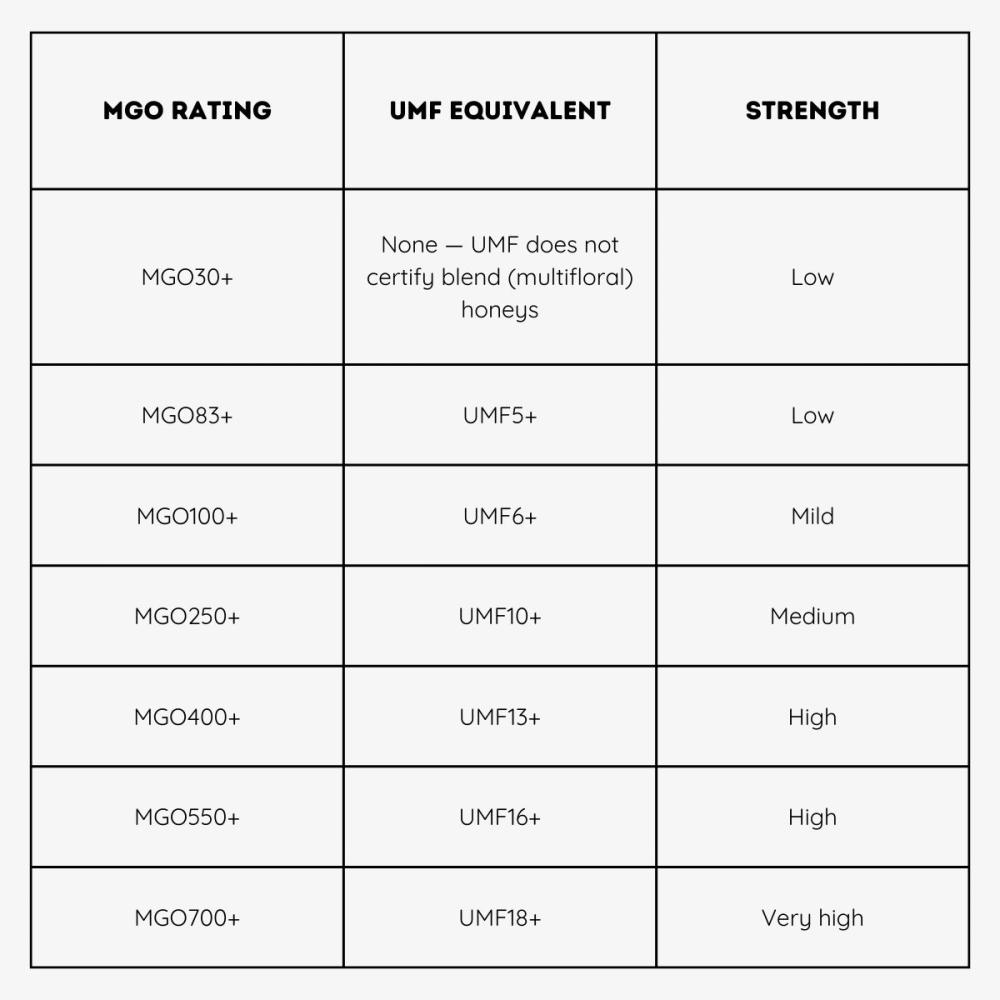
Methylglyoxal (MGO), the compound that provides the key antibacterial properties in manuka honey can be measured. This grading system only measures the level of the one compound: Methylglyoxal. The number after “MGO” on a bottle refers to the quantity of methylglyoxal in mg/kg. For example, a level of MGO263+ means that there is at least 263mg of methylglyoxal per kilo of honey.
There are limitations to this system, as methylglyoxal levels can be synthetically raised through heating. The normal range of MGO can be between 83-1046, with MGO83 being equivalent to UMF5+.
UMF Grading of Manuka Honey:
UMF, or Unique Manuka Factor, serves as a standardised measure to verify the authenticity of Manuka Honey from New Zealand. This comprehensive and independently certified indicator is globally recognised as a quality assurance system for ensuring that the Manuka Honey is genuine and from New Zealand. The range is normally between 5 and 25 for UMF.
This grading system comprises of 4 different tests which measure key markers in the honey to ensure that the MGO level will remain the same during its shelf life, and tests for potency, authenticity, shelf-life, and freshness. The 4 signature compounds that it tests for are Leptosperin, DHA, MGO and HMF. Leptosperin is only found in the nectar of manuka, and so is a guarantee that the honey is genuine.
What is the difference between MGO and UMF?
While MGO testing focuses solely on methylglyoxal, UMF testing offers a more thorough assessment using accredited lab-testing of the honey’s purity, shelf-life, and potency by examining four specific compounds, including leptosperin – a crucial indicator of genuine New Zealand origin.
Both methods allow the customers to see the methylglyoxal content within the honey. Unlike MGO, the UMF grading system cannot be synthetically altered by heating the honey. UMF testing stands out as a more robust system, providing customers with assurance regarding the authenticity and potency of the honey. The UMF grading system authenticates and guarantees that the level of chemical markers is what is stated on the label.
Additionally, MGO testing does not identify if the manuka honey is monofloral and so sources can be varied, from Manuka, Kanuka and Multifloral origin.
Manuka Honey Product Recommendations:
The Tahi New Zealand Manuka Honey with a UMF of 15+ and a MGO of 514+ is a honey which is less sweet than lower UMF honeys, with more "savoury" flavours. It is rich, tasty and moderately tangy. It acts as a superfood which can help boost the immune system, support gut health and overall well-being. It is suitable for vegetarians and independently certified and tested to have a UMF of 15+ and an MGO of 514.
The Tahi New Zealand 100% Manuka Honey Lozenges with a UMF of 15+ and a MGO activity of 514+ are deliciously soothing with a sweet yet subtly tangy taste. These lozenges help soothe coughs, colds and sore throats, as well as provide a natural energy boost.
Summary:
- Manuka Honey is native to New Zealand and must be exclusively sourced from Manuka flower nectar to be called Manuka Honey.
- Manuka honey offers more antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties due to higher levels of Methylglyoxal (MGO), lower levels of hydrogen peroxide and a richer concentration of flavonoids and phenolic compounds than regular honey.
- Abundant levels of MGO, flavonoids, and phenols contribute to health benefits, including wound healing, infection prevention, pain relief, and potential support for a healthy gut.
- Manuka Honey is graded by MGO or UMF, with MGO indicating Methylglyoxal levels, and UMF providing a comprehensive assessment of purity, shelf-life, and potency through accredited lab-testing for 4 key compounds: MGO, DHA, Leptosperin and HMF.
By Saarah Mengrani, MSc Biotechnology