Collagen: Everything You Need To Know | Complete Guide
Collagen supplements have become increasingly popular for their potential benefits in promoting healthier skin, joints, hair, and nails. Additionally, they have been scientifically proven beneficial for health conditions such as menopause, osteoarthritis, and sarcopenia. However, with so many options on the market, it’s important to understand how they work, the right dosage, and any precautions to take before incorporating them into your routine. In this compelete guide, we’ll address some common questions about collagen, including why some people might not see results, the potential risks of taking too much, and whether it’s safe to use during pregnancy. Read on to learn how collagen can benefit your overall health and wellness.
Collagen supplements available to buy: click here.
What It Is & Sources of Collagen | Beauty and Health Benefits
Menopause, Osteoarthritis, Sarcopenia
Supplements & Recommendations | How To Take and Dosage | Collagen Skincare | FAQ
What is Collagen?
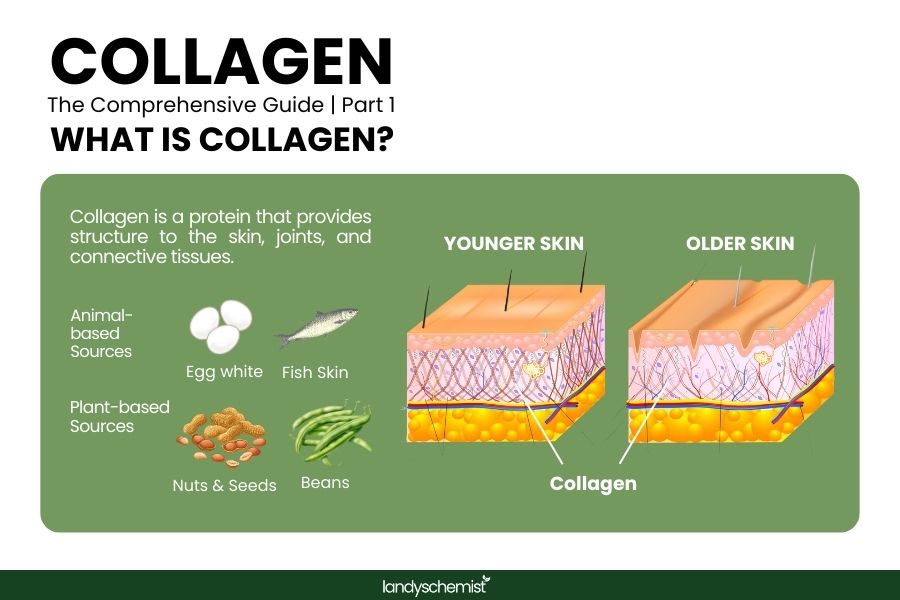
Collagen is a structural protein that plays a crucial role in providing strength and elasticity to various tissues in the body, including the skin, bones, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage. It is the most abundant protein in the human body, making up about one-third of its total protein content. Collagen acts as a scaffold, helping tissues maintain their shape and integrity. As we age, the production of collagen in the body decreases, which can lead to wrinkles, joint pain, and other age-related issues.
Sources Of Collagen
Animal-Based Collagen Sources
Animal-based foods are rich in collagen, especially types I and II. Fish, particularly the skin and scales, provides type I collagen, which supports skin health. Egg whites are rich in proline, an amino acid important for collagen production. Bone broth, chicken skin, and cartilage are also excellent collagen sources, supporting both skin and joint health.
Plant-Based Collagen Sources
While plants don’t contain collagen, they provide nutrients that help boost collagen production. Nuts and seeds are high in zinc and omega-3 fatty acids, both essential for collagen synthesis. Leafy greens, citrus fruits, and garlic are rich in vitamin C and sulphur, which are vital for collagen formation.
Collagen Supplements
Collagen supplements, available in tablets, capsules, powders, and liquids, are a convenient way to increase collagen intake. These supplements are typically derived from animal sources and can help support skin and joint health with easy absorption, especially in powdered or liquid form.
Collagen Beauty and Health Benefits

As the most extensive protein in the body, collagen plays a vital role in supporting gut health, joint health, and the overall strength of our skin, hair, and nails.
Skin Health:
Collagen is the main structural component of the skin, found in the dermis. It works alongside elastin, another protein, to provide structure, firmness, and elasticity, as well as allowing it to maintain hydration and a smooth, plump texture. As collagen fibers form a network in the skin, they help maintain the skin's integrity, giving it strength and a smooth texture. Over time, the body produces less collagen, and the existing collagen fibres start to break down. This leads to wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging.
- Read more: Best Collagen Supplement for Sagging Skin
- SHOP: Collagen skincare products
- Everything you need to know about Collagen & Skincare
Hair & Nails:
Collagen provides essential amino acids for keratin production, the protein that is responsible for hair and nail health. As collagen helps maintain the structure of the nail bed, while also promotes hair growth. Decreasing collagen levels with age can lead to nails becoming weaker and more prone to damage.
Joint Health:
Collagen plays a key role in joint health by forming the cartilage that cushions the bones and allows for smooth movement. This cartilage acts as a shock absorber, preventing bones from rubbing together during physical activity. As collagen production slows down with age, cartilage can become weaker, leading to joint pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
Bone Strength:
Collagen is a major component of bone structure, providing flexibility and strength. It forms a framework for bones, allowing minerals like calcium and phosphorus to bind and form a dense, strong structure. It also helps bones absorb impact and resist fractures. By supporting collagen production, bone strength can be maintained, reducing brittleness and helping preserve bone density.
Gut Health:
Collagen plays a crucial role in maintaining gut health by strengthening the lining of the digestive tract. It supports the integrity of the intestinal walls, promoting a healthy gut lining and preventing "leaky gut", a condition where undigested particles can enter the bloodstream. Collagen helps repair damaged tissues in the digestive system, making it important for those suffering from digestive issues such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). It also aids in digestion by supporting the muscles of the digestive tract, helping with nutrient absorption and overall gut function.
Heart Health:
Collagen is essential for maintaining the structure and function of blood vessels, including arteries, veins, and capillaries. It provides the flexibility and strength necessary for these vessels to expand and contract, which supports healthy circulation. Collagen helps keep blood vessels from becoming stiff and brittle, which can lead to high blood pressure and cardiovascular disease. Adequate collagen levels are important for the heart, as they help prevent artery damage, maintain smooth blood flow, and support overall cardiovascular health.
Collagen for Health Conditions
Collagen for Menopause
During menopause, the body undergoes significant hormonal changes, leading to symptoms such as skin aging, joint pain, and bone density loss. Collagen is a crucial component in maintaining skin elasticity, so as its production decreases, skin becomes more prone to wrinkles and sagging. Supplementing with collagen can help restore hydration and elasticity, reducing the appearance of fine lines. Collagen also plays a key role in joint health by maintaining cartilage integrity, which can help alleviate joint pain and stiffness, common in menopausal women. Additionally, collagen supports bone strength by helping maintain bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
Collagen for Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease where the cartilage that cushions the joints breaks down over time, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness. Collagen is a critical component of cartilage, and supplementing with collagen can help protect and repair damaged cartilage, providing relief from OA symptoms. In people with osteoarthritis, collagen supplementation can stimulate the production of new cartilage, which helps cushion the joints and reduce friction between bones. By supporting cartilage repair and reducing inflammation, collagen helps improve joint function, making it easier to perform everyday activities.
Collagen for Sarcopenia
Sarcopenia – by definition – is the age-related loss of muscle mass, strength, and function, often starting around the age of 30 and accelerating with age. As muscle mass decreases, it can lead to frailty, weakness, and difficulty performing daily tasks. Collagen is an important structural protein in muscles, tendons, and connective tissues. Supplementing with collagen provides the amino acids necessary for muscle repair and regeneration. Studies have shown that collagen supplementation can increase muscle mass and strength in individuals with sarcopenia by stimulating muscle protein synthesis.
Best Collagen Supplements

When choosing a collagen supplement, it’s essential to consider the source, quality, and additional ingredients that enhance its effectiveness. Look for hydrolysed collagen peptides for better absorption, and choose products that support skin, joint health, and overall vitality. It's also important to select supplements with beneficial additions like vitamin C, which aids absorption, and hyaluronic acid, which promotes skin hydration. Read more our blog on the benefits of taking Vitamin C with Collagen.
What to Look for When it Comes to Collagen Supplements
- Hydrolysed Collagen Peptides: Ensures better absorption and effectiveness.
- Vitamin C & Hyaluronic Acid: Enhance collagen absorption and improve skin hydration.
- Sustainably Sourced: Choose responsibly sourced collagen, such as grass-fed bovine or wild-caught marine collagen.
- Additional Nutrients: Look for extra ingredients like amino acids and biotin to boost skin, hair, and nail health.
- Read more: Ultimate Guide to Collagen Supplements
What to Avoid in Collagen Supplements
- Excessive Fillers & Additives: Avoid supplements with unnecessary sugars, sweeteners, or artificial ingredients.
- Synthetic Preservatives: Choose clean, preservative-free collagen products.
Collagen Recommendations:
Shop our range of Collagen Supplements here.
Bovine Collagen
- Source: Grass-fed, pasture-raised cows
- Type: Type I and Type III collagen
- Additional Features: Flavourless and easy to mix into drinks or food
- Read our comprehensive review: Ancient + Brave True Collagen
Marine Collagen:
- Source: Wild-caught fish
- Type: Type I collagen
- Additional Features: Includes hyaluronic acid and vitamin C for enhanced collagen synthesis
Vegan Collagen
- Source: Plant-based ingredients that stimulate collagen production
- Additional Features: Contains vitamin C, biotin, and amino acids to support collagen synthesis
How To Take Collagen & Dosage
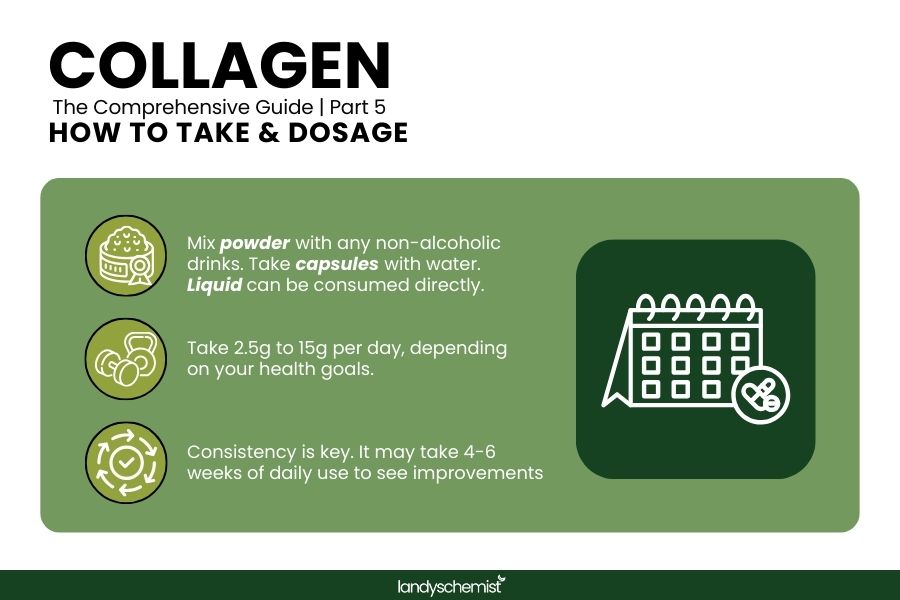
For the best absorption, it’s recommended to take collagen on an empty stomach or with vitamin C (which aids collagen synthesis).
- Powder: Mix with water, coffee, smoothies, or other beverages.
- Capsules: Take as directed, usually with water.
- Liquid: Can be consumed directly or mixed into your drinks.
Recommended Collagen Dosage:
Typically, 2.5g to 15g per day is effective, depending on your health goals:
- For Skin & Joint Health: A standard dose is around 5g per day, which can help improve skin elasticity, reduce wrinkles, and support joint comfort.
- If you’re taking collagen to support muscle recovery after workouts, consider 10g per day. Collagen can help repair muscle tissue and support joint health, making it ideal for those who engage in regular physical activity.
Be sure to follow the recommended dosage on the packaging, as some collagen types may have different concentrations. For noticeable results, consistency is key, and it may take 4-6 weeks of daily use to see improvements
Collagen as a Skincare Ingredient
Collagen is a powerhouse ingredient in skincare, known for its ability to enhance skin elasticity and reduce signs of ageing. Often paired with hyaluronic acid, it boosts hydration levels, keeping skin plump and smooth. Found in products like skincare collagen cream, collagen works to firm the skin, minimise fine lines, and support overall skin health. Embracing the benefits of collagen can elevate your routine, promoting a youthful, radiant complexion.
The Difference Between Collagen in Skincare and Collagen Supplements
Collagen as a skincare ingredient works topically, focusing on hydrating and smoothing the outer layers of the skin. It often forms a protective barrier, locking in moisture and temporarily improving skin’s appearance by reducing fine lines and boosting elasticity. In contrast, collagen as a supplement works from within, targeting the deeper dermal layers. Once ingested, it is broken down into amino acids or peptides, which stimulate the body’s natural collagen production, promoting long-term improvements in skin elasticity, hydration, and overall health. While topical collagen offers quick, surface-level benefits, supplements address skin health at its core for more enduring results.
Best Collagen Skincare Products
Shop our range of Collagen Skincare here.
Vichy LiftActiv Collagen Specialist Cream
Formulated to target collagen loss, this cream restores skin firmness and reduces signs of ageing across all skin types.
Eucerin Hyaluron-Filler + Elasticity Day SPF30
Infused with collagen-supporting ingredients, this cream enhances skin elasticity while protecting against UV damage.
Filorga Lift-Structure Anti-Ageing Ultra Lifting Cream
Enriched with collagen-boosting compounds, this cream visibly firms and lifts skin for a more youthful appearance.
FAQ’s
Does Collagen work?
Collagen supplements may not work for everyone due to individual differences in absorption and metabolism. In some cases, the body may not absorb the collagen efficiently, or the collagen may not be from a high-quality source. Additionally, collagen works best when paired with other supportive nutrients like vitamin C, and results may take several weeks to become noticeable. For maximum benefit, it's important to choose a high-quality collagen supplement and follow recommended dosages consistently.
Do Collagen Supplements Have Side Effects?
Can You Take Too Much Collagen?
While collagen is generally safe, taking excessive amounts can lead to digestive issues such as bloating, heartburn, or a feeling of fullness. It’s recommended to stay within the recommended dosage (usually 2.5g to 15g per day). Taking significantly more than this won’t necessarily result in better outcomes and may cause discomfort. Always follow the dosage instructions on your specific supplement or consult a healthcare professional if unsure.
Does Collagen Help You Lose Weight?
Collagen is not a direct weight loss supplement, but it can support weight loss indirectly. By improving muscle mass and joint health, collagen can help improve workout performance, allowing for better exercise results. It also helps maintain skin elasticity, which can prevent sagging when losing fat. Additionally, collagen may help control appetite by promoting satiety, potentially reducing overall calorie intake. However, for effective weight loss, a balanced diet and regular exercise are essential.
Can You Take Collagen While Pregnant?
Collagen is generally considered safe during pregnancy, as it’s a naturally occurring protein in the body. However, it’s important to ensure that the collagen supplement is of high quality and free from harmful additives or contaminants. Consulting with a healthcare provider before taking any supplements during pregnancy is always advisable to ensure the safety of both the mother and baby. Some brands may also offer collagen specifically formulated for pregnant women, ensuring they meet safety and nutritional standards.
Can I get Halal collagen?
Yes, absolutely. Pura Collagen is a high quality halal-certified collagen brand that targets specific health needs.
For more frequently asked questions about collagen (e.g., Is it good to take collagen every day? Or, Can collagen cause itchy skin), check out our blog here.
References
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6432532/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9947798/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7827176/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535346/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25721900/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10058045/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37064452/
- https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/what-bone
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9198822/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9198822/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10691097/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5429168/
- https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/osteoarthritis
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4066461/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4594048/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8944283/