CoQ10 for Boosting Fertility & Reproductive Success
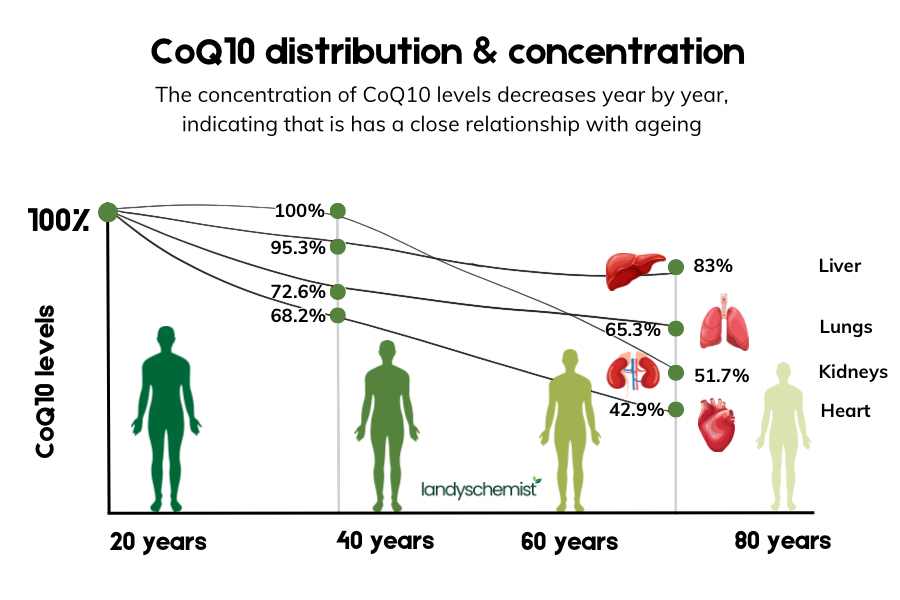
CoQ10, or Coenzyme Q10, is a powerful antioxidant found naturally in every cell of the body. As we age, our natural levels of CoQ10 decrease, which can result in lower energy levels, fatigue, and signs of ageing.
CoQ10 supplements offer a simple and effective way to support fertility in both men and women by improving egg quality in women and enhancing sperm health in men. In addition to its reproductive benefits, CoQ10 may also support overall health by boosting energy levels, promoting heart health, and protecting the skin from oxidative damage.

Jump to section
- How does CoQ10 work for fertility?
- CoQ10 fertility benefits for women
- CoQ10 fertility benefits for men
- Dosage & guidelines
- When to start and stop taking CoQ10
- Who will benefit from CoQ10 the most
- CoQ10 fertility success
How does CoQ10 work for fertility & reproduction?
CoQ10 works in the body by improving mitochondrial function. Mitochondria are the tiny powerhouses within our cells, responsible for generating the energy needed for cellular processes, including reproduction1. In women, it helps strengthen egg quality by providing energy for proper maturation, while in men, CoQ10 enhances sperm motility and overall function. As CoQ10 levels naturally decline with age, supplementation replenishes these levels, improving reproductive health and increasing the chances of conception.
While it can take several weeks to see noticeable improvements in fertility, consistent use of CoQ10 supplements helps to promote a better environment for both egg and sperm health. CoQ10 also acts as an antioxidant, protecting reproductive cells from oxidative stress, which can also hinder fertility chances.
CoQ10 Fertility benefits for women
- Egg Quality: CoQ10 supports mitochondrial function in eggs, ensuring they have the energy needed for proper maturation.Higher quality eggs are crucial for successful fertilisation and pregnancy. Research has shown that CoQ10 supplementation can improve egg quality, particularly in women over 35, who may experience a decline in egg quality as they age2.
- Ovarian Health & IVF Response: CoQ10 supplementation has been shown to improve ovarian response during fertility treatments, such as IVF. By increasing the energy available to the ovaries, CoQ10 may help to improve the quality and quantity of eggs retrieved, which can lead to better outcomes during assisted reproductive technology (ART)3,4.
- Healthy Ovulation: CoQ10 may regulate hormonal balance, which plays a key role in ensuring regular and healthy ovulation. Proper ovulation is essential for conception, and CoQ10 may assist in balancing the hormones responsible for egg release, boosting fertility potential5.
- Reduces Oxidative Stress: As an antioxidant, CoQ10 helps protect eggs from oxidative damage caused by free radicals. Oxidative stress can damage eggs, impair fertilisation, and reduce the chances of pregnancy. By reducing oxidative stress, CoQ10 may help to create a better environment for egg health and successful fertilisation6.
- Supports PCOS & Endometriosis Fertility: CoQ10 may help women with PCOS and endometriosis by improving egg quality and regulating hormone levels. Additionally, CoQ10 may help thicken the uterine lining, which is crucial for successful implantation and pregnancy in women with these conditions. Research suggests CoQ10 supplementation could support better fertility outcomes in women with both PCOS and endometriosis7,8.
CoQ10 Fertility benefits for men
- Sperm Quality: CoQ10 plays a critical role in improving sperm motility, morphology (shape), and count. This is particularly important as sperm quality is a major factor in male fertility. Studies have shown that CoQ10 supplementation can enhance sperm health, leading to better chances of successful conception9.
- Sperm Motility: CoQ10 helps increase the energy production within sperm cells, improving their ability to swim and reach the egg for fertilisation. This enhanced motility is key for increasing the chances of sperm successfully navigating the female reproductive tract and achieving fertilisation10.
- Reduces Oxidative Stress: Oxidative stress can damage sperm DNA, leading to poor sperm function and reduced fertility. A 2024 study concluded that CoQ10 supplementation improves sperm parameters, reduces oxidative stress markers, and decreases sperm DNA fragmentation in infertile males11.
- Increases Sperm Count: Some studies have suggested that CoQ10 supplementation can increase sperm count in men with low sperm concentration. By boosting the overall health of sperm cells, CoQ10 helps improve sperm production and quality, leading to better fertility outcomes12.
The available research strongly supports the role of CoQ10 supplementation in improving fertility and reproductive health in both men and women. By enhancing critical aspects such as egg and sperm quality, motility, and mitigating oxidative stress, CoQ10 helps to promote an optimal environment for conception.
Coq10 fertility dosage

Research suggests a CoQ10 dosage for fertility typically ranges between 100mg to 600mg per day. However, the safe and recommended daily dosage is generally between 100mg and 200mg, depending on factors such as age, gender, and individual health conditions.
- For Women: A daily dose of 200mg to 300mg has been shown to improve egg quality, particularly for women over 35 or those undergoing fertility treatments like IVF.
- For Men: A dosage of 200mg to 400mg per day is effective in improving sperm quality and motility.
Recommended CoQ-10 supplement for fertility:
CoQ10 Dosage for Those Over 40
For both men and women over 40, a higher dosage of 300mg to 600mg per day is often recommended. This higher dose supports the body's increased need for energy and mitochondrial function as egg quality tends to decline with age.
When start and stop taking coq10 for fertility:
Women and men should start taking CoQ10 supplements 2-3 months before trying to conceive to improve egg and sperm quality. For women undergoing fertility treatments, such as IVF, CoQ10 should typically be taken throughout the treatment cycle, but it’s important to stop after successful conception or upon the advice of a healthcare provider
It's recommended to stop taking CoQ10 once you're pregnant, unless advised otherwise by a healthcare provider. Some studies suggest that CoQ10 may not be necessary during early pregnancy, and in some cases, it could interfere with certain medications.
Who May Benefit from CoQ10 for Fertility the most:
- Couples Undergoing IV
- Women with PCOS
- Women with endometriosis
- Men with low sperm count or motility
- Both men and women over 35+ who are trying for a baby
Coq10 fertility success
CoQ10 supplements have shown valuable support for improving fertility, supported by numerous studies highlighting its positive effects on egg and sperm quality, motility, and overall reproductive health. CoQ10 helps create a healthier environment for conception, particularly for those facing age-related fertility challenges.
"CoQ10 has shown promising benefits in supporting fertility by improving egg quality and sperm health, which are critical factors for successful conception," says Girish Desai, Pharmacist at Landys Chemist. “Its ability to boost energy production at the cellular level makes it a key supplement for individuals looking to optimise their reproductive health."
Disclaimer:
This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for medical advice. Consult your doctor or healthcare provider before starting any supplements, treatments, or remedies. Ensure a varied and balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle before considering supplements. Supplements should not replace a balanced diet.
Sources:
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10030209/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8431086/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29587861/
- https://www.fertstert.org/article/S0015-0282%2815%2901517-4/fulltext
- https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202407.0879/
- https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/pharmacology/articles/10.3389/fphar.2022.936233/full
- https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/25/12/6298
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35941510/
- https://www.auajournals.org/doi/10.1016/j.juro.2009.02.121
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/and.13570
- https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/pharmacology/articles/10.3389/fphar.2024.1497930/
- https://wjmh.org/DOIx.php?id=10.5534%2Fwjmh.190145